Market Overview
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is at the forefront of a transformative shift in cancer treatment. Unlike traditional treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted drugs, CAR-T cell therapy harnesses the body’s own immune system to combat malignant cells. By genetically engineering a patient’s T-cells to express specific receptors (CARs) that recognize cancer antigens, this groundbreaking therapy has opened new doors in the treatment of hematological malignancies and holds significant promise for solid tumors.
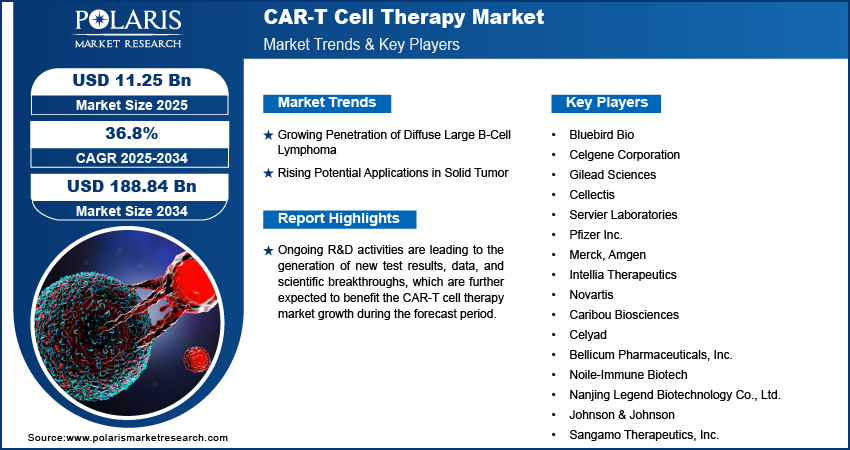
In 2024, the global CAR-T cell therapy market was valued at USD 7.31 billion, reflecting its rapid emergence as a mainstream therapeutic option. The market is projected to surge to USD 11.25 billion in 2025, and reach an astounding USD 188.84 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.8% during the forecast period (2025–2034). This meteoric rise highlights the increasing adoption of CAR-T therapies across various clinical settings and the immense research and commercial potential within the space.
Market’s Growth Drivers
Several powerful forces are fueling the unprecedented growth of the CAR-T cell therapy market:
- Rising Incidence of Cancer
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. With an increasing number of cancer diagnoses, particularly blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, there is an urgent demand for more effective and personalized treatment options. CAR-T therapy has demonstrated exceptional response rates in patients with relapsed or refractory blood cancers, positioning it as a crucial solution in oncology.
- Advancements in Gene Engineering and Cell Therapy
Technological innovations in genetic engineering, particularly CRISPR and other genome-editing tools, have streamlined the modification of T-cells. These advancements have led to improved safety profiles, better targeting, and enhanced efficacy of CAR-T therapies. Additionally, scalable and efficient manufacturing platforms have significantly reduced production costs and turnaround times.
- Regulatory Approvals and Expanding Indications
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA and EMA have approved several CAR-T therapies for different types of cancers. These include Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel), Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel), and Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel). As clinical trials continue to validate the efficacy of CAR-T in new indications—including solid tumors—regulatory pathways are becoming more streamlined, encouraging faster market entry for new products.
- Strategic Collaborations and Investments
Biopharmaceutical giants and research institutions are actively investing in CAR-T development. Strategic alliances, licensing agreements, and mergers are common across the industry, fostering innovation and expanding the global footprint of these therapies. Investment in CAR-T startups and clinical-stage companies is also accelerating research and commercialization efforts.
- Personalized and Precision Medicine Trends
CAR-T therapy epitomizes the shift toward personalized medicine by utilizing a patient’s own immune cells to target disease. As precision medicine gains traction, healthcare providers and patients alike are seeking more tailored, effective treatments—driving demand for CAR-T solutions.
Key Trends in the CAR-T Cell Therapy Market
- Allogeneic (“Off-the-Shelf”) CAR-T Therapies
Currently, most CAR-T therapies are autologous—derived from a patient’s own cells. However, allogeneic CAR-T, which uses donor-derived T-cells, is gaining traction for its potential to lower costs and shorten production times. Companies like Allogene Therapeutics and CRISPR Therapeutics are at the forefront of this shift, aiming to revolutionize CAR-T manufacturing and accessibility.
- Expansion into Solid Tumors
While hematologic cancers remain the primary indication for CAR-T therapies, researchers are actively investigating their efficacy in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, breast cancer, and pancreatic cancer. Overcoming challenges such as tumor microenvironment barriers and antigen heterogeneity is central to this expansion.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence in CAR-T Development
AI and machine learning are increasingly being employed to design optimal CAR constructs, predict patient response, and enhance clinical trial efficiency. These technologies are streamlining drug discovery pipelines and improving therapy customization.
- Emergence of Combination Therapies
Combining CAR-T therapy with checkpoint inhibitors, kinase inhibitors, or radiation is being explored to overcome resistance mechanisms and boost treatment efficacy. These synergistic strategies are likely to expand therapeutic windows and extend CAR-T’s reach.
- Globalization of CAR-T Trials and Manufacturing
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, is emerging as a major hub for CAR-T development, with numerous trials and biomanufacturing facilities. The region’s cost-effective research capabilities and strong governmental support are accelerating its market participation.
Research Scope and Clinical Development
The research landscape for CAR-T cell therapy is vast and highly dynamic. As of 2025, hundreds of clinical trials are underway globally, investigating various CAR designs, co-stimulatory domains, and target antigens. Some major research directions include:
- Dual-Targeting CARs: To prevent tumor escape by antigen loss, dual-antigen targeting CARs are being developed.
- Armored CAR-Ts: These engineered cells secrete cytokines or express proteins that enhance persistence and resistance to immunosuppression.
- Logic-Gated CARs: These CARs activate only in the presence of multiple tumor markers, improving specificity and reducing off-target effects.
- Universal CAR Platforms: These allow for “plug-and-play” targeting of different antigens using a common CAR backbone, streamlining development across cancers.
Beyond oncology, researchers are exploring CAR-T applications in autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and even organ transplantation tolerance, showcasing its versatile therapeutic potential.
Market Segmentation
To better understand the structure of the CAR-T cell therapy market, it can be segmented by:
- By Target Indication
- Hematologic Malignancies
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Multiple Myeloma
- Solid Tumors
- Glioblastoma
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Breast Cancer (Emerging)
- Others
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Infectious Diseases (under investigation)
- By Product Type
- Autologous CAR-T
- Allogeneic CAR-T (off-the-shelf)
- By End User
- Hospitals & Cancer Centers
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Biopharmaceutical Companies
- By Region
- North America
Dominates the market due to early approvals, strong R&D, and presence of key players. - Europe
Significant investments in advanced therapies and regulatory incentives. - Asia-Pacific
Fast-growing CAR-T development ecosystem, especially in China. - Latin America and Middle East & Africa
Emerging markets with growing focus on advanced oncology treatments.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its potential, CAR-T therapy faces several hurdles:
- High Cost and Accessibility: Treatment costs can exceed USD 400,000, limiting access in low- and middle-income countries.
- Manufacturing Complexities: Autologous CAR-T production is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- Safety Concerns: Risk of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity remains significant, though increasingly manageable.
- Reimbursement Barriers: Payers are still navigating how to fairly and sustainably reimburse for these high-cost therapies.
Looking ahead, innovation in manufacturing (e.g., automation, point-of-care production), better safety profiling, and global expansion are expected to ease these concerns. As the industry evolves, CAR-T is likely to become more mainstream, not only in cancer treatment but also in broader areas of immune modulation.
Conclusion
The CAR-T cell therapy market is on the brink of a transformative decade. With a staggering projected growth from USD 11.25 billion in 2025 to USD 188.84 billion by 2034, the therapy represents more than just a cancer treatment—it signifies a paradigm shift in how medicine interacts with the human immune system.
Propelled by technological advancements, regulatory momentum, and an unrelenting demand for personalized care, CAR-T therapy is poised to redefine the future of treatment for cancer and beyond. As science continues to evolve, so too will the opportunity to save and extend lives through the power of engineered immunity.