Market Overview
Thyroid cancer, a relatively rare yet increasingly prevalent form of endocrine malignancy, has witnessed a notable uptick in diagnosis rates over the past few decades. As awareness rises and diagnostic technologies evolve, the thyroid cancer diagnostics market is emerging as a vital segment within the global oncology diagnostics industry.
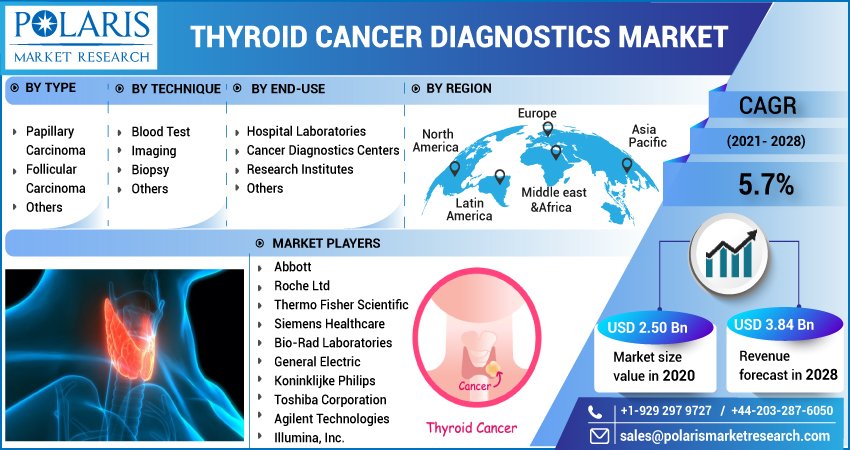
Valued at USD 2.50 billion in 2020, the global thyroid cancer diagnostics market is projected to expand steadily at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% during the forecast period. This growth is propelled by a confluence of factors such as technological advancements in imaging and molecular testing, rising incidences of thyroid nodules, and increased access to healthcare services across emerging economies.
The market encompasses a wide spectrum of diagnostic tools including ultrasound, fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB), radionuclide scans, blood tests for thyroid function, and molecular assays that help distinguish benign from malignant nodules. With the growing precision and accessibility of these tools, early diagnosis and personalized treatment of thyroid cancer are becoming increasingly feasible.
Market Growth Drivers
- Rising Prevalence of Thyroid Cancer and Nodular Disease
Although thyroid cancer accounts for only a small percentage of total cancer diagnoses, its incidence has been on a sharp rise, particularly in developed countries. According to the American Cancer Society, thyroid cancer is among the most rapidly increasing cancers in the United States. Much of this increase is attributed to the improved detection of small, subclinical papillary carcinomas via imaging. The rising incidence of thyroid nodules, especially in women and the elderly, is driving the demand for accurate and reliable diagnostic modalities.
- Advances in Imaging and Molecular Diagnostics
The diagnostic landscape is evolving rapidly with high-resolution ultrasound, elastography, and hybrid imaging techniques (PET-CT, SPECT-CT) enabling the detection of even small thyroid lesions. Moreover, molecular diagnostic tools, such as gene expression classifiers and next-generation sequencing (NGS), are enhancing diagnostic precision by differentiating between benign and malignant nodules. These innovations significantly reduce unnecessary surgeries and support more tailored treatment approaches.
- Awareness Campaigns and Screening Programs
Public health campaigns and increasing media coverage of thyroid health have encouraged routine checkups and proactive screening, especially in high-risk groups. Consequently, more patients are being diagnosed at earlier stages, often when tumors are still asymptomatic. This has contributed to the growth of the diagnostics market.
- Growing Geriatric Population
With aging being a known risk factor for several types of cancer, including thyroid cancer, the expanding global geriatric population is expected to fuel diagnostic demand. Older individuals are more likely to undergo screening for nodular goiter and thyroid dysfunction, further driving market growth.
- Technological Integration in Healthcare
The integration of AI-based diagnostic support systems, digital pathology, and tele-radiology services is optimizing workflows, reducing diagnostic delays, and increasing accuracy. These systems assist pathologists and radiologists in interpreting thyroid biopsies and scans more effectively, improving overall diagnostic confidence.
Key Market Trends
- Shift Towards Minimally Invasive Diagnostics
Technological advancements are enabling less invasive yet highly accurate diagnostic methods. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) remains the gold standard for evaluating thyroid nodules, but innovations like core-needle biopsy and liquid biopsy are gaining ground for specific cases. These techniques minimize patient discomfort and complication risks while providing sufficient cellular material for analysis.
- Rise of Molecular and Genomic Testing
Molecular testing has transformed thyroid nodule evaluation, particularly in indeterminate cases (Bethesda category III or IV). Tests like the Afirma Genomic Sequencing Classifier (GSC) and ThyroSeq enable clinicians to determine malignancy risk based on genetic alterations. These diagnostics reduce unnecessary surgeries and guide the selection of targeted therapies, marking a major shift toward personalized oncology.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Imaging
AI is being increasingly deployed in thyroid ultrasound imaging for automatic detection and classification of nodules. Deep learning algorithms can differentiate benign from malignant nodules with high accuracy, thereby supporting radiologists in clinical decision-making and reducing diagnostic variability.
- Expanding Role of Companion Diagnostics
With the advent of targeted therapies for aggressive or refractory thyroid cancers (e.g., RET inhibitors), the role of companion diagnostics is becoming critical. These diagnostics identify patients who are likely to benefit from specific treatments based on genetic mutations, further enhancing the demand for precision testing.
- Growing Adoption of Home-based and Remote Testing
While still in early development stages, companies are exploring home sample collection kits and tele-diagnostics platforms that could make thyroid function and biomarker testing more accessible. This is particularly relevant in the context of telehealth expansion and post-COVID-19 care models.
Research Scope and Innovation Outlook
Research in thyroid cancer diagnostics is centered around improving sensitivity, specificity, and patient outcomes. Key areas of focus include:
- Multi-omics Profiling: Combining genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics to gain a holistic understanding of tumor biology and enhance diagnostic accuracy.
- Liquid Biopsy Development: Detecting circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and other biomarkers from blood samples for non-invasive monitoring and recurrence detection.
- Biomarker Discovery: Identifying novel biomarkers for aggressive subtypes like anaplastic thyroid cancer to support early detection and treatment planning.
- Artificial Intelligence Applications: Developing AI platforms for risk stratification based on imaging and clinical features.
- Cost-effective Diagnostic Platforms: Innovating affordable diagnostic kits for use in resource-limited settings to promote equitable care access.
Market Segmentation
A granular understanding of the thyroid cancer diagnostics market can be obtained through the following segmentation:
- By Diagnostic Technique
- Imaging Techniques
- Ultrasound
- CT/MRI
- PET/SPECT Scans
- Biopsy & Cytology
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB)
- Core Needle Biopsy
- Blood Tests
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Thyroglobulin (Tg) & Anti-Tg Antibodies
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Gene Expression Classifiers
- Mutation Panels (e.g., BRAF, RAS, RET/PTC)
- By Cancer Type
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
- Other Rare Types
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Cancer Research Centers
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Specialty Clinics
- By Region
- North America
- Largest market share due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, high screening rates, and strong R&D investments.
- Europe
- Significant growth driven by national cancer registries, universal healthcare, and early detection programs.
- Asia-Pacific
- Fastest-growing region fueled by rising thyroid disease prevalence, medical tourism, and healthcare infrastructure expansion.
- Latin America & Middle East and Africa
- Emerging markets with increasing diagnostic awareness and international collaboration in oncology care.
Challenges and Restraints
Despite steady market growth, several challenges persist:
- Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment: With improved imaging, many indolent tumors are being diagnosed that may never cause symptoms. This can lead to unnecessary biopsies or surgeries.
- False Positives in Cytology: FNAB can yield indeterminate or non-diagnostic results, leading to diagnostic uncertainty.
- Access and Affordability: High costs of molecular testing and limited availability in low-resource settings can hamper widespread adoption.
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: Accurate interpretation of imaging and cytology requires experienced professionals, which may be lacking in some regions.
Competitive Landscape
The thyroid cancer diagnostics market is competitive and innovation-driven. Key players are focusing on technological enhancements, strategic partnerships, and geographic expansion. Notable companies include:
- Roche Diagnostics
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Abbott Laboratories
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- GE Healthcare
- Philips Healthcare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Veracyte, Inc.
- Beckman Coulter (Danaher)
- Quest Diagnostics
These companies are at the forefront of developing next-generation diagnostics and expanding their portfolios to include molecular assays and AI-integrated imaging solutions.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the thyroid cancer diagnostics market is expected to witness continued expansion, driven by innovations in personalized medicine, artificial intelligence, and patient-centered diagnostic approaches. Integration of diagnostic data across imaging, molecular, and biochemical domains will enable clinicians to make faster, more informed decisions, improving outcomes for patients globally.
Additionally, as global health systems shift toward value-based care, early and accurate diagnostics will play a pivotal role in optimizing treatment strategies, reducing unnecessary interventions, and lowering overall healthcare costs.
With robust research pipelines, growing public awareness, and favorable regulatory landscapes, the thyroid cancer diagnostics market is well-positioned for a future defined by precision, accessibility, and improved patient care.
Conclusion
The global thyroid cancer diagnostics market is not just a component of the broader oncology field—it is a dynamic arena that reflects the convergence of innovation, clinical need, and patient empowerment. As new technologies emerge and access expands, the ability to detect thyroid cancer accurately and early will continue to improve, driving both clinical outcomes and market value.
More Trending Latest Reports By Polaris Market Research:
Lactic And Poly Lactic Acid Market
North America Reverse Osmosis Equipment Market
Enterprise Content Management Market
Lemon Oil and Lemon Extracts Market
Europe Renewable Methanol Market