Market Overview
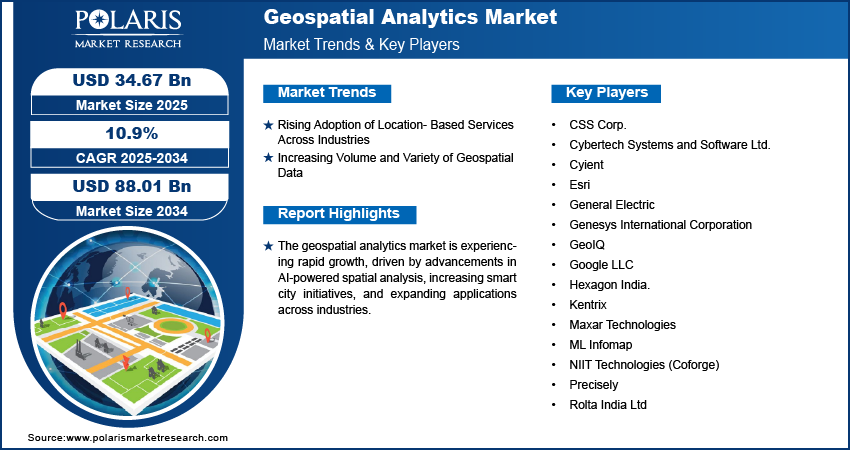
In an increasingly data-driven world, the ability to extract actionable insights from location-based data has become vital across numerous industries. Geospatial analytics, which involves the collection, display, and manipulation of imagery, GPS, satellite photography, and historical data, is transforming how organizations understand space, behavior, and interaction within physical environments. The global geospatial analytics market stood at USD 31.33 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow robustly to USD 88.01 billion by 2034. This anticipated growth, at a CAGR of 10.9% from 2025 to 2034, reflects the rapid adoption of geospatial intelligence in sectors like agriculture, defense, real estate, retail, logistics, and smart city planning.
As organizations seek to enhance operational efficiency, optimize resources, and drive innovation, geospatial analytics is becoming a critical component of strategic decision-making. Fueled by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and cloud computing, the field is witnessing a revolution in both scope and scale. From tracking pandemics and managing supply chains to monitoring environmental changes, the use of geospatial tools has never been more expansive or essential.
𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐡𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐇𝐞𝐫𝐞:
https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/geospatial-analytics-market
Market’s Growth Drivers
- Integration with Emerging Technologies
One of the most significant factors driving growth in the geospatial analytics market is the integration with cutting-edge technologies such as AI, machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G. These technologies enhance the capability of geospatial systems to deliver real-time, predictive, and highly granular insights. AI and ML algorithms, for instance, allow for faster pattern recognition and anomaly detection in spatial datasets, which is crucial in applications like natural disaster prediction and urban planning.
- Rising Demand for Location Intelligence
With the surge in mobile device usage and IoT-enabled infrastructure, location data is being generated at unprecedented levels. Businesses are increasingly leveraging this data for customer analytics, targeted marketing, asset tracking, and risk management. In retail, for instance, geospatial analytics helps identify optimal store locations, analyze footfall, and improve supply chain logistics.
- Government Investments and Smart City Initiatives
Governments worldwide are investing heavily in geographic information systems (GIS) and spatial data infrastructures as part of smart city development and public safety initiatives. These systems support critical services such as traffic monitoring, infrastructure management, waste management, and emergency response. For example, geospatial platforms can be used to optimize emergency response routes during natural disasters, thereby saving lives and resources.
- Climate Change and Environmental Monitoring
Climate change and environmental degradation are driving demand for accurate environmental monitoring tools. Geospatial analytics plays a crucial role in tracking deforestation, glacial melting, air and water pollution, and wildlife migration. The ability to visualize and predict environmental changes helps policy-makers and conservationists make informed decisions and implement targeted interventions.
- Military and Defense Applications
Defense and intelligence agencies are among the earliest adopters of geospatial technology, using it for surveillance, battlefield awareness, mission planning, and national security. As geopolitical tensions rise globally, demand for advanced geospatial solutions in defense applications continues to grow, further fueling the market.
Key Trends in the Geospatial Analytics Market
- Shift to Cloud-Based Platforms
Cloud computing is transforming the way geospatial data is stored, processed, and accessed. Cloud-based GIS platforms offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and remote access, making them particularly appealing to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These platforms facilitate collaboration, improve data-sharing, and enable real-time analytics across distributed teams and locations.
- Real-Time Data Analytics
The ability to analyze spatial data in real-time is becoming a game-changer, particularly for industries that rely on dynamic information, such as transportation, logistics, and disaster management. Real-time analytics allows for faster response to changing conditions—such as traffic congestion, weather patterns, or security threats—leading to improved operational efficiency and decision-making.
- Proliferation of UAVs and Remote Sensing Technologies
The rise in the use of drones and satellites equipped with high-resolution sensors has dramatically increased the availability of real-time, high-accuracy geospatial data. These technologies are now widely used in agriculture, mining, infrastructure inspection, and emergency response. They enhance data collection while reducing time and operational costs.
- Geospatial Data Democratization
Previously restricted to experts and government agencies, geospatial tools are now becoming more accessible to non-specialists through user-friendly platforms and visualization tools. This democratization allows a broader range of stakeholders—including business executives, planners, and even consumers—to engage with and leverage spatial insights.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns
As geospatial analytics grows, so too do concerns about data privacy and ethical usage. The collection and use of location-based data, particularly personal movement data, raise significant questions around consent, surveillance, and data protection. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR are pushing companies to adopt more transparent and secure data practices.
Research Scope and Analytical Coverage
The research scope of the geospatial analytics market is broad, encompassing a wide range of data types, tools, techniques, and applications. Key research areas include:
- Spatial Data Collection: Methods such as GPS, LiDAR, remote sensing, and mobile mapping systems.
- Data Processing & Visualization: Use of GIS platforms, 3D modeling, thematic mapping, and heat maps to interpret spatial data.
- Predictive Modeling: Leveraging historical and real-time data to forecast future scenarios in urban development, environmental shifts, or consumer behavior.
- Application-Specific Research: Tailored studies on agriculture (e.g., precision farming), health (e.g., disease spread modeling), transportation (e.g., route optimization), and energy (e.g., site suitability analysis for renewable projects).
The field is inherently interdisciplinary, bringing together experts from geography, computer science, data analytics, environmental science, and urban planning. As such, advancements in one area often have cross-sectoral benefits, spurring innovation across multiple domains.
Market Segmentation
The geospatial analytics market can be segmented based on various parameters, including component, type, deployment mode, application, and industry vertical.
By Component
- Software: GIS software, remote sensing software, spatial analysis tools, data visualization platforms.
- Hardware: GPS devices, drones, imaging sensors, servers.
- Services: Consulting, integration, maintenance, and training services.
By Type
- Surface Analytics
- Network Analytics
- Geovisualization
- Geocoding & Reverse Geocoding
By Deployment Mode
- On-Premise
- Cloud-Based
Cloud-based deployments are witnessing faster growth due to their scalability and cost-efficiency.
By Application
- Surveying & Mapping
- Urban Planning
- Disaster Risk Reduction
- Health & Epidemiology
- Agriculture Monitoring
- Defense & Intelligence
- Transportation & Logistics
By Industry Vertical
- Government & Public Safety
- Energy & Utilities
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Healthcare
- Telecommunications
- Manufacturing
- Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI)
The agriculture and urban planning sectors are particularly fast-growing, driven by sustainability goals and food security concerns.
Conclusion
Geospatial analytics is no longer a niche technology reserved for cartographers or defense strategists—it’s now a cornerstone of modern decision-making across industries. As the market surges toward a projected USD 88.01 billion valuation by 2034, it is clear that spatial intelligence will be instrumental in shaping the future of business, governance, sustainability, and innovation.
Driven by rapid technological advancement, increased demand for real-time insights, and growing global challenges that require spatial understanding, geospatial analytics is positioned as a vital tool for both the public and private sectors. However, to fully harness its power, organizations must also navigate challenges related to data privacy, infrastructure, and skill development.
In the years ahead, the organizations that best understand and implement geospatial intelligence will lead in areas ranging from climate resilience and infrastructure planning to personalized marketing and resource optimization—proving that in the world of data, location really is everything.
𝐁𝐫𝐨𝐰𝐬𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐬:
AI-Powered Enterprise Automation Market
Asia Pacific Radiopharmaceuticals Market
Joint Replacement Devices Market
High Protein Bakery Products Market
Livestock Identification Market
Grain Oriented Electrical Steel Market
𝐁𝐫𝐨𝐰𝐬𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐀𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐥𝐞𝐬: