The Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) market is experiencing robust momentum globally, driven by the growing emphasis on sustainable energy technologies, stringent emission reduction mandates, and increasing investments in high-efficiency electrochemical conversion systems. As the world transitions away from fossil fuels, SOFCs are emerging as a critical technology in the race toward carbon neutrality.
Capable of delivering high efficiency, low emissions, and versatile fuel compatibility, SOFCs are increasingly being adopted in both commercial and residential applications for distributed power generation. Their potential to seamlessly integrate with hydrogen, natural gas, and biofuels is adding to their appeal across utility, industrial, and mobility sectors.
Market Overview
Solid oxide fuel cells are advanced energy conversion devices that use a ceramic electrolyte to convert chemical energy from fuel into electricity through an electrochemical conversion process — without combustion. Operating at high temperatures (typically between 600°C to 1000°C), SOFCs boast high electrical efficiency (up to 60%) and even higher overall system efficiency (up to 85%) when waste heat is utilized.
Unlike conventional power generation systems, SOFCs offer scalable, silent, and low-maintenance solutions. Their modular nature makes them ideal for stationary fuel cell systems in off-grid, microgrid, and combined heat and power (CHP) applications.
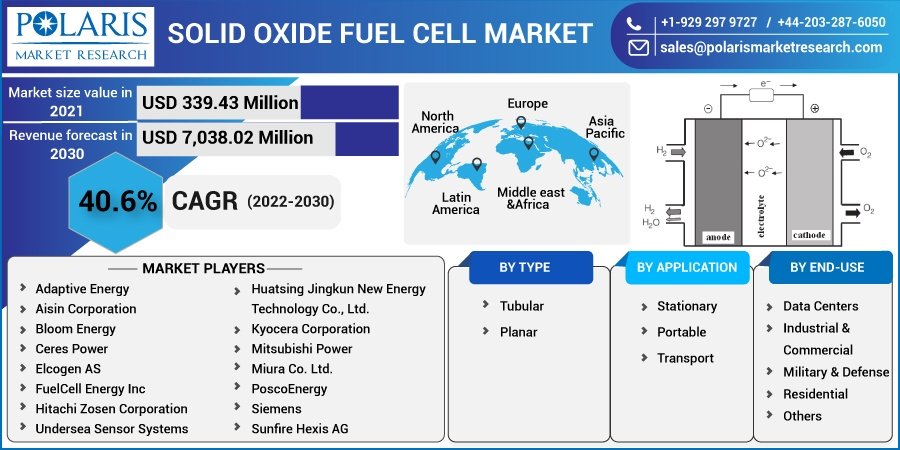
According to the research report, the global solid oxide fuel cell market was valued at USD 339.43 million in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 7,038.02 million by 2030, to grow at a CAGR of 40.6% during the forecast period.
Key Market Growth Drivers
1. Decentralized Energy Demand
The rising demand for reliable, off-grid, and distributed power generation is significantly contributing to SOFC market growth. From remote data centers to rural electrification and urban microgrids, the ability of SOFCs to operate autonomously and efficiently makes them an attractive solution for decentralized power infrastructure.
Governments and private utilities are increasingly investing in microgrid systems for energy resilience — especially in regions vulnerable to extreme weather events and grid instability.
2. Hydrogen Economy Momentum
As nations double down on clean hydrogen as a cornerstone of their decarbonization strategies, SOFCs are gaining traction due to their fuel flexibility. While they can operate on natural gas, biogas, and syngas, SOFCs are especially well-suited for electrochemical conversion of hydrogen, producing electricity with near-zero emissions.
R&D advancements are further enhancing compatibility with green hydrogen, reinforcing SOFCs as a core technology in hydrogen-based energy ecosystems.
3. Energy Efficiency and Emissions Reduction
Compared to internal combustion engines and traditional power plants, SOFCs offer significantly higher energy efficiency and minimal environmental impact. Their quiet operation, low vibration, and absence of harmful pollutants (like NOx, SOx, and particulates) make them ideal for use in urban areas and enclosed spaces.
This aligns well with global clean energy mandates, carbon neutrality goals, and ESG objectives — making SOFCs a preferred solution for industrial and residential customers seeking sustainability and cost savings.
4. Technological Innovation and Scale-up
Breakthroughs in ceramic electrolyte materials, stack design, and thermal management systems have enhanced the durability, performance, and affordability of SOFC systems. The integration of advanced ceramics, metal supports, and 3D-printed components is reducing startup times and operational degradation, extending system life to 40,000–60,000 hours.
Additionally, large-scale demonstration projects and public-private partnerships are helping bring SOFC systems from laboratory-scale to mass-market deployment, fostering commercialization and competitiveness.
Browse Full Insights:
https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/solid-oxide-fuel-cell-market
Market Challenges
Despite favorable conditions, the SOFC market faces several obstacles that may impede accelerated growth:
1. High Initial Cost
SOFC systems involve expensive components such as advanced ceramics and high-temperature sealants, making them more capital-intensive than some conventional technologies. The high cost of system manufacturing and integration continues to be a barrier to widespread adoption — particularly in developing economies.
2. Thermal Management and Durability
Operating at high temperatures leads to thermal cycling issues, material degradation, and challenges in long-term durability. Innovations in thermal insulation and ceramic electrolyte stabilization are underway, but SOFCs still face performance issues under variable load conditions and start-stop cycles.
3. Fuel Infrastructure Limitations
Although SOFCs are compatible with hydrogen and various hydrocarbon fuels, a lack of fueling infrastructure — especially for hydrogen — limits their application. Development of a robust hydrogen supply chain is crucial to fully unlock the potential of SOFC technologies.
4. Complexity of System Integration
Integrating SOFCs into existing power grids or combined systems (e.g., with batteries or solar panels) requires complex controls and monitoring systems. Installation and maintenance demand skilled labor and advanced diagnostics, which can limit scalability for small users.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America continues to lead the global SOFC market, driven by innovation, strong public funding, and growing use in stationary fuel cell applications. The U.S. government’s emphasis on energy independence and grid modernization, along with investments in hydrogen hubs, is fostering rapid SOFC deployment.
Several states have enacted tax credits, R&D grants, and clean energy procurement programs supporting fuel cell adoption in public facilities, hospitals, and critical infrastructure.
Europe
Europe represents a highly progressive SOFC market, bolstered by the EU’s “Fit for 55” initiative and the Green Deal. Countries such as Germany, the UK, and the Netherlands are heavily investing in clean hydrogen and fuel cell innovation. The European Hydrogen Backbone initiative and the IPCEI hydrogen projects provide direct support for SOFC technology development.
European applications range from residential CHP units to large-scale distributed power generation systems in industrial zones and transportation corridors.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing SOFC market, led by countries like Japan, South Korea, China, and India. Japan and South Korea have made significant headway in commercializing SOFC-based home energy systems, driven by energy security concerns and long-term sustainability goals.
China is expanding its fuel cell industry as part of its Five-Year Plan and is promoting SOFCs in urban heating and industrial power. India’s focus is on integrating SOFCs into its rural electrification and hydrogen mobility missions.
Latin America
Latin America is emerging as a nascent market for SOFCs, primarily through pilot projects in Brazil, Chile, and Argentina. The region’s interest in reducing reliance on diesel generators and improving energy access in remote areas is generating demand for small-scale stationary fuel cells and microgrids.
Middle East & Africa
In the Middle East and parts of Africa, SOFCs are being explored as part of clean desalination, industrial processing, and grid-resilient infrastructure. The UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are investing in hydrogen and fuel cell technologies to support decarbonization and diversify energy sources.
Key Companies and Strategic Developments
Several companies are driving innovation and adoption in the global SOFC market. They are focusing on:
-
Enhancing stack performance and lowering cost per kW.
-
Developing modular SOFC systems for commercial and residential applications.
-
Integrating SOFCs with hydrogen reformers and heat recovery systems.
-
Establishing partnerships with utilities and clean tech developers for large-scale deployment.
Strategic initiatives include investments in automated manufacturing, localized supply chains, and new business models (such as fuel cell-as-a-service) to accelerate market penetration.
Conclusion
The global Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Market stands at a pivotal juncture. With the world urgently seeking alternatives to fossil fuels, SOFCs offer an attractive mix of efficiency, sustainability, and flexibility. Their use in electrochemical conversion and distributed power generation applications aligns seamlessly with 21st-century energy needs.
Backed by technological innovation, policy support, and rising awareness about climate impacts, the market is well-positioned to play a central role in the clean energy transition. Continued advances in ceramic electrolyte design, material science, and fuel infrastructure will be essential in overcoming existing barriers and unlocking the full potential of SOFCs across the globe.
More Trending Latest Reports By Polaris Market Research:
Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market
Glass Bonding Adhesives Market
Neurostimulation Devices Market: An Electrical Stimulation Technology to Cure Several Conditions