Market Overview
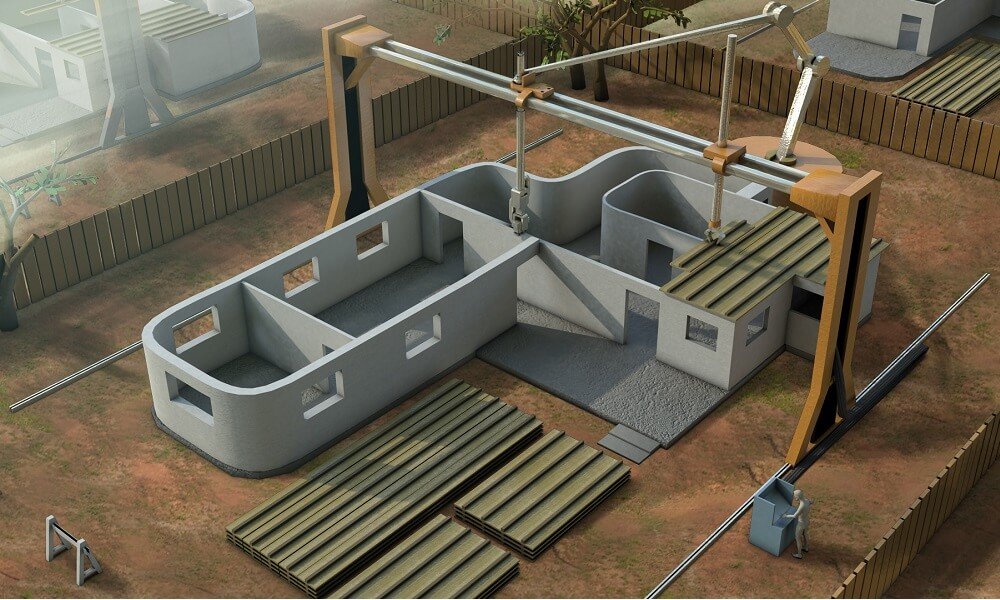
3D Printing Construction Market, also referred to as additive manufacturing in construction, involves the layer-by-layer creation of building structures using robotic arms or gantry systems. This innovative technique allows for precise, cost-effective, and sustainable construction by reducing waste, labor dependency, and construction time. This growth is driven by technological advances, the need for affordable housing, and growing environmental awareness. Governments, real estate developers, and non-profit organizations are increasingly adopting concrete 3D printing for quick, efficient, and green construction solutions.
According to the research report published by Polaris Market Research, the 3D Printing Construction Market Size Is Expected To Reach USD 10,756.4 thousand in 2022, and is anticipated to generate an estimated revenue of USD 6021.5 million at a CAGR of 88.3% during the forecast period.
Key Market Growth Drivers
- Demand for Affordable and Rapid Housing Solutions
Global urbanization and population growth have intensified the demand for affordable and fast-deployable housing. 3D printing construction enables the creation of entire homes within 24 to 48 hours, making it an ideal solution for low-income housing and emergency shelter projects. Using automated building techniques, firms can reduce manual labor costs, eliminate human error, and optimize material usage.
In regions affected by natural disasters or refugee crises, 3D-printed buildings offer a rapid and cost-effective way to provide shelter. The ability to print structures on-site using local or recyclable materials further enhances its viability in remote or resource-constrained areas.
- Sustainability and Waste Reduction
The growing global emphasis on green building practices has positioned sustainable construction technology as a core value in infrastructure development. Traditional construction methods account for a significant portion of global carbon emissions and material waste. 3D printing construction, by contrast, produces minimal waste due to its precise, on-demand material usage.
Additionally, many companies are exploring the use of recycled plastics, bio-based composites, and geopolymer concrete as alternative materials, further minimizing the ecological footprint. The synergy between 3D printing and eco-friendly construction aligns well with the sustainability goals of governments and developers.
- Technological Advancements in Construction Robotics
Modern concrete 3D printing equipment has seen rapid evolution in terms of scalability, precision, and material compatibility. Advances in robotics, machine learning, and design software have enabled the creation of complex architectural designs that were once impossible with conventional methods.
Cutting-edge printers can now build multi-story structures, bridges, and modular units with embedded plumbing and electrical systems. The integration of building information modeling (BIM) and IoT sensors allows for real-time quality control and predictive maintenance, enhancing project efficiency and lifespan.
- Reduction in Construction Time and Labor Dependency
Time and labor costs are two of the most critical challenges in traditional construction. 3D printing significantly reduces the need for large construction crews and shortens building timelines. By adopting automated building techniques, developers can maintain consistent quality, improve worker safety, and meet project deadlines with greater accuracy.
With global labor shortages affecting the construction sector—especially in developed economies—3D printing is emerging as a scalable solution to bridge the gap and keep large-scale projects on track.
Browse Full Insights:
https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/3d-printing-construction-market
Market Challenges
Despite the positive outlook, the 3D printing construction market faces a few significant hurdles:
- High Initial Investment and Infrastructure Requirements
Setting up a 3D printing construction operation involves considerable capital investment. Costs associated with purchasing large-scale printers, developing proprietary materials, and training personnel can be prohibitive, particularly for small and medium-sized construction firms.
Moreover, construction sites must be equipped with reliable power sources, transport logistics, and environmental controls to support additive manufacturing in construction, especially for larger projects or in remote locations.
- Regulatory and Code Compliance
Building codes, safety regulations, and permit processes have not yet fully adapted to 3D printing construction. The lack of standardized testing procedures and certification mechanisms across regions can delay project approvals or limit adoption.
Governments and regulatory bodies are beginning to explore frameworks for evaluating 3D-printed buildings, but until a global standard emerges, inconsistent compliance will remain a bottleneck.
- Limited Material Diversity and Structural Limitations
While concrete 3D printing dominates the market, the availability of suitable and structurally validated printing materials remains limited. Most systems are optimized for specific mixes, and alternative materials (e.g., recycled composites or bio-based polymers) require extensive R&D and certification.
In addition, 3D printing methods currently face challenges in printing reinforcements (such as steel) and finishing multi-story buildings without hybrid manual interventions. These limitations must be overcome to scale the technology to high-rise and commercial developments.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America is a leader in the 3D printing construction space, driven by technological innovation, supportive government initiatives, and a strong focus on sustainable urban development. Several pilot projects involving residential housing, military barracks, and disaster relief shelters have successfully demonstrated the technology’s potential.
The United States, in particular, is investing in large-scale sustainable construction technology to address its housing shortage and aging infrastructure. Additionally, collaborations between academic institutions and construction tech firms are fueling continuous innovation in materials and processes.
Europe
Europe’s commitment to environmental sustainability and smart cities has made it an attractive market for 3D printing construction. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark have been early adopters of automated building techniques, using them to construct public buildings, commercial spaces, and eco-villages.
The European Union’s Green Deal and Circular Economy Action Plan are further boosting investment in technologies that promote low-carbon and resource-efficient construction.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid urbanization, infrastructural investments, and smart city initiatives in countries such as China, India, South Korea, and Singapore.
China has already showcased some of the largest 3D-printed buildings, including multi-story apartment complexes, while India’s government is exploring the use of concrete 3D printing to build affordable homes under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) scheme.
Growing populations and housing deficits are creating strong incentives for faster and greener construction methods across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East is emerging as a strong adopter, particularly in the UAE and Saudi Arabia, where futuristic urban planning and mega-projects like NEOM demand innovative construction technologies. Dubai aims to have 25% of new buildings constructed using 3D printing by 2030, making it a global hub for additive manufacturing in construction.
In Africa, 3D printing is being explored for low-cost housing and disaster response shelters, offering a practical solution to socio-economic challenges and infrastructure deficits.
Key Companies
Several pioneering companies are shaping the global 3D printing construction market by investing in R&D, expanding international projects, and forming strategic partnerships. These firms specialize in developing large-format printers, proprietary concrete mixtures, and integrated construction platforms.
- ICON: A key player in the U.S., ICON is widely recognized for its innovation in building affordable housing using concrete 3D printing. The company has successfully collaborated with NGOs, government bodies, and defense agencies to construct homes and military barracks.
- COBOD International: Based in Denmark, COBOD is known for its scalable 3D construction printers and has been involved in projects across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. The company supports automated building techniques tailored to commercial, residential, and utility applications.
- Apis Cor: Apis Cor has made headlines for printing the world’s first fully functional house using a mobile printer. The firm focuses on sustainable, cost-efficient solutions for urban and remote environments and is expanding its footprint globally.
These companies are driving the shift from traditional to digital construction, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the built environment.
Conclusion
The 3D Printing Construction Market is at the forefront of a construction revolution—offering an answer to the global demand for faster, cheaper, and greener building methods. From residential housing to large-scale infrastructure, additive manufacturing in construction is paving the way for a future where design freedom, material efficiency, and sustainability coexist.
More Trending Latest Reports By Polaris Market Research:
Voluntary Carbon Credit Market
Research Department Explosives Market: A Reliable Substitute for Torpedoes and Aerial Bombs