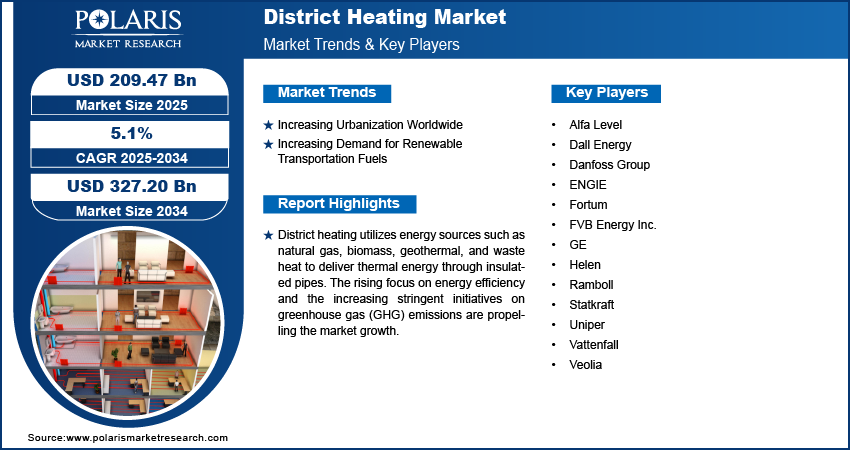
The global District Heating Market is undergoing a significant transformation as urbanization, decarbonization mandates, and innovations in combined heat and power technologies drive demand for efficient, large-scale thermal networks. Valued at USD 209.47 billion in 2025, the market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2025 through 2034, reaching an estimated SD 327.20 billion by 2034. This press release offers a market overview and summary, explores key growth drivers and challenges, and delivers an in-depth regional analysis. Four Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords—heat networks, waste heat recovery, geothermal district heating, and energy efficiency solutions—are integrated to enhance thematic relevance.
Market Overview / Summary
District heating systems distribute thermal energy—typically in the form of hot water or steam—from centralized plants to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers through a network of insulated pipes. Core technologies include boiler-based plants, combined heat and power (CHP) units that co-generate electricity and heat, and emerging renewable sources such as geothermal district heating and biomass-fired boilers.
By end-use, heat networks serve space heating, domestic hot water, and industrial process heat. In Europe, district heating accounts for over 10% of total heat demand, while mature markets in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe exceed 50% penetration in urban areas. North America and Asia-Pacific are witnessing rapid market development, fueled by sustainability initiatives and government incentives. Key stakeholders include utilities, municipal authorities, engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) firms, and technology providers specializing in energy efficiency solutions for network optimization and consumer metering.
Advances in digital controls, leak detection, and thermal storage are enhancing network reliability and reducing non-revenue water (heat losses). Coupled with evolving regulatory frameworks encouraging carbon emission reductions, district heating is positioned as a cornerstone of future urban energy systems.
Key Market Growth Drivers
- Decarbonization and Renewable Integration
Governments worldwide are setting net-zero targets, spurring the transition from fossil-fuel boilers to low-carbon district heating. The integration of geothermal district heating projects and biomass CHP plants reduces carbon intensity while leveraging local renewable resources. In countries like Iceland and Sweden, over 80% of district heat originates from renewable or waste heat sources, showcasing the technology’s decarbonization potential. - Urbanization and Infrastructure Modernization
Rapid urban growth in Asia-Pacific and Latin America is straining existing heating infrastructures. District heating offers a scalable solution for high-density cities, reducing per-capita energy consumption by up to 30% compared to individual boilers. Governments in China and India are prioritizing large-scale heat network rollouts under smart-city initiatives, allocating subsidies for network expansion and incentivizing private-sector participation. - Advancements in Waste Heat Recovery
Industrial facilities and data centers generate substantial excess heat that can be captured through waste heat recovery systems and fed into district networks. Integration of waste heat from steel mills, cement plants, and data parks not only improves overall plant efficiency but also lowers district heating fuel costs and emissions. Policymakers are enacting regulations that encourage industry-to-heat-network connections, unlocking new growth avenues. - Digitalization and Smart Network Management
The deployment of IoT-enabled sensors, advanced analytics, and dynamic pricing models enhances network performance and customer engagement. Real-time monitoring of flow rates, temperature differentials, and pipeline integrity supports proactive maintenance and demand forecasting. Energy efficiency solutions—such as weather-compensated control and consumer load management—optimize network supply, reducing heat losses by up to 15%.
Market Challenges
- High Capital Investment and Long Payback Periods
Establishing district heating infrastructure—including central plants, distribution mains, and consumer substations—requires significant upfront capital, often in the range of USD 2,000–3,500 per household equivalent. Long payback periods, typically 7–12 years, can deter municipal and private investors without strong policy support or guaranteed heat offtake agreements. - Regulatory and Tariff Complexities
District heating is regulated differently across jurisdictions, with tariff-setting mechanisms varying between cost-plus models and competitive tenders. Misaligned incentives—such as subsidized gas prices—can undermine the economic case for network expansion. Achieving regulatory harmonization and transparent pricing frameworks is essential to attract investment and protect consumer interests. - Technical Hurdles in Retrofitting
Integrating district heating into existing urban fabric involves complex civil works, rights-of-way negotiations, and disruptions to traffic and residents. Retrofitting heritage districts or dense downtown cores demands innovative trenchless technologies and stakeholder engagement to minimize social and economic impacts. - Seasonal Demand Variability
Heating demand peaks during winter months, leading to underutilization of network capacity in shoulder seasons. Thermal storage solutions—such as large-scale hot water tanks or phase-change materials—can buffer demand fluctuations but add to project costs. Balancing capacity sizing and storage investment is critical to optimize system economics.
Key Market Players:
- Alfa Level
- Dall Energy
- Danfoss Group
- ENGIE
- Fortum
- FVB Energy Inc.
- GE
- Helen
- Ramboll
- Statkraft
- Uniper
- Vattenfall
- Veolia
𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐡𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐇𝐞𝐫𝐞 @ https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/district-heating-market
Polaris Market Research has segmented the district heating market report based on energy source, application, technology:
By Energy Source Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Renewable Energy
- Fossil Fuels
- Waste Heat
By Application Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By Technology Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Conventional District Heating
- Smart District Heating
Regional Analysis
Europe
Europe leads the District Heating Market, representing 45% of global capacity in 2024. Denmark and Sweden exemplify mature heat network ecosystems, with 64% and 61% urban penetration, respectively. The EU’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and Energy Efficiency Directive mandate member states to increase renewable heat shares and modernize aging networks. Germany, the U.K., and the Netherlands are accelerating CHP installations and waste heat integration in metropolitan regions.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with a projected CAGR of 8.1% through 2030, accounting for 25% of the market. China’s 14th Five-Year Plan commits to expanding district heating by 15% in northern cities, while Japan and South Korea are piloting geothermal district heating zones. India’s National Thermal Energy Efficiency Strategy includes grants for network feasibility studies and consumer metering, laying the groundwork for robust market uptake.
North America
North America holds 18% of global market share, driven by retrofits in U.S. college campuses (e.g., Cornell University’s lake-source cooling and heating) and expansions in Canadian cities like Edmonton. Policy drivers include state-level decarbonization goals and federal tax credits for renewable thermal projects. Private-sector utilities are investing in CHP and waste heat recovery integrations to diversify their service offerings.
Latin America
Latin America represents 7% of the market. Brazil’s industrial corridor in São Paulo features bioenergy-powered heat networks, while Chile explores urban networks to leverage geothermal resources in the Andes. Economic volatility and limited financing options remain challenges, but multilateral development banks are offering concessional loans to catalyze projects in Argentina and Colombia.
Middle East & Africa (MEA)
The MEA region accounts for 5% of global capacity. Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations—particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia—are evaluating district cooling and heating hybrids to optimize desalination-powered thermal grids. South Africa is piloting biomass CHP-based networks in agricultural regions, supported by renewable energy regulations and rural electrification programs.
Conclusion
The District Heating Market is poised for sustained growth, underpinned by the convergence of urbanization, decarbonization policies, and technological innovation in combined heat and power, geothermal district heating, and waste heat recovery. While high capital costs and regulatory complexities pose obstacles, advances in digital network management and supportive policy frameworks are unlocking new opportunities. Europe will continue to lead in maturity and scale, but Asia-Pacific and Latin America promise the most rapid expansion. By aligning infrastructure investments with energy efficiency solutions and stakeholder collaboration, district heating stands to become a linchpin of sustainable urban energy systems worldwide.
More Trending Latest Reports By Polaris Market Research:
Treatment Planning Systems And Advanced Image Processing Market
EV Connector Market: An Electric Power Transfer for Effective Charging
Industrial Control Systems Security Market
Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture Market