Market Overview
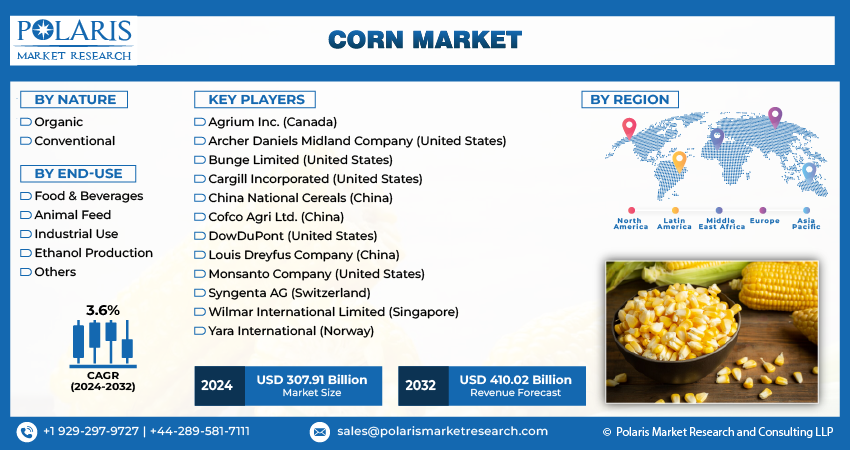
The global corn market continues to be a vital pillar of the agricultural economy, driven by its versatility as a staple food crop, animal feed component, and industrial raw material. Corn, also known as maize, is among the most cultivated crops worldwide and serves as a crucial commodity for both developed and developing nations. The global corn market size is expected to reach USD 410.02 billion by 2032, according to a new study by Polaris Market Research.
Corn’s multifaceted applications range from food production and livestock nutrition to ethanol-based fuel and biodegradable plastics. The increasing emphasis on renewable energy sources and food security, coupled with advancements in agricultural biotechnology, are significantly influencing market dynamics.
Key Market Growth Drivers
1. Rising Demand for Animal Feed
A primary driver of corn market growth is its essential role in livestock feed demand. Corn is a rich source of carbohydrates and serves as a primary feed grain for cattle, poultry, and swine. With the global population continuing to grow, especially in developing regions, the demand for animal protein is accelerating.
This surge in meat consumption is directly boosting corn consumption. The expansion of commercial livestock farming, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, is anticipated to further elevate demand for high-energy feed products, keeping corn in strong demand.
2. Growth of the Ethanol Biofuel Industry
Corn plays a significant role in the ethanol biofuel industry, particularly in countries like the United States and Brazil, which use corn-based ethanol as a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. Governments across the globe are promoting renewable energy policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thereby increasing ethanol blending mandates.
The energy sector’s shift towards low-carbon fuels has fueled investments in corn-based ethanol production. As oil prices fluctuate and carbon reduction goals intensify, the demand for ethanol is expected to continue driving corn utilization on an industrial scale.
3. Expansion in Processed Food and Beverage Industry
Corn is widely used in the food and beverage industry in various forms, including cornmeal, corn starch, corn oil, and high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS). The growing preference for processed and convenience foods has led to a steady increase in corn-derived ingredient consumption.
Additionally, the rise in global disposable incomes and changing dietary preferences have expanded the market for corn-based food products, particularly in baked goods, snacks, and sweeteners.
4. Advances in Agricultural Biotechnology and Corn Production Trends
Modern biotechnology has enabled the development of genetically modified (GM) corn varieties with enhanced resistance to pests, herbicides, and environmental stresses. These advancements have improved yields, reduced crop losses, and made large-scale cultivation more economically viable.
The integration of precision farming techniques, smart irrigation systems, and satellite monitoring is optimizing corn production trends, especially in regions with high-tech agricultural infrastructure. These innovations are helping farmers enhance productivity and sustainability, driving market expansion.
Key Companies in the Global Corn Market
The global corn market is characterized by a combination of multinational agribusinesses, biotech firms, and regional producers. Key market players include:
1. Cargill Incorporated
Cargill is a global agribusiness leader engaged in corn procurement, processing, and trading. The company is heavily involved in corn syrup, ethanol, and animal feed production.
2. Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM)
ADM operates extensive corn milling facilities and is a major supplier of corn-based ingredients for food, industrial, and energy markets.
3. Bunge Limited
Bunge is active in corn trading and processing across North and South America. The company supplies feed-grade and food-grade corn to various markets.
4. Bayer AG (Crop Science Division)
Through its acquisition of Monsanto, Bayer offers genetically modified corn seeds with traits for pest resistance and drought tolerance.
5. DuPont de Nemours, Inc. (Corteva Agriscience)
Corteva is a major seed producer providing hybrid corn varieties along with crop protection solutions.
6. Syngenta AG
Syngenta develops high-yield corn hybrids and crop protection chemicals, serving both commercial growers and smallholder farmers globally.
Other notable players include Louis Dreyfus Company, KWS Saat SE, Limagrain, and GROWMARK Inc.
𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐡𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐇𝐞𝐫𝐞: https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/corn-market
Market Challenges
1. Fluctuations in Agricultural Commodity Prices
The corn market is significantly influenced by agricultural commodity prices, which are prone to volatility due to weather patterns, geopolitical tensions, trade policies, and global demand-supply dynamics. Unexpected droughts, floods, or frost can severely affect yields and supply chains.
Moreover, tariff disputes and trade restrictions—such as those between the U.S. and China in recent years—can cause uncertainty in corn exports and imports, impacting global market stability and farmer profitability.
2. Environmental Concerns and Land Degradation
Large-scale corn farming, particularly monoculture practices, has raised concerns regarding soil degradation, biodiversity loss, and increased use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Intensive corn cultivation can lead to nutrient depletion, water overuse, and higher greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable agricultural practices and eco-friendly crop rotation systems are needed to mitigate the long-term environmental impact of corn production. Growing consumer and regulatory pressures for sustainability may require significant shifts in farming methodologies.
3. Competition from Alternative Crops and Feed Ingredients
Corn faces competition from alternative feed grains such as sorghum, barley, and wheat, which are often substituted based on availability and pricing. Similarly, in the biofuel sector, sugarcane and cassava-based ethanol provide viable alternatives to corn ethanol in certain markets.
The diversification of feed and energy crops presents a challenge to long-term dominance of corn in specific applications, particularly in regions focused on reducing dependence on a single crop.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America, particularly the United States, remains the largest producer and exporter of corn globally. The U.S. Corn Belt—encompassing states like Iowa, Illinois, Nebraska, and Indiana—accounts for a significant portion of the world’s corn production. The region benefits from advanced farming technologies, GM seed adoption, and a robust ethanol industry.
Canada and Mexico are also vital players in the North American corn trade, with Mexico being a major importer of U.S. corn for food and feed purposes.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the corn market, led by countries such as China, India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. China is both a leading producer and consumer, with corn being a crucial component of its massive animal husbandry sector. India’s corn production is growing due to increased hybrid seed usage and demand from the poultry feed industry.
Population growth, urbanization, and rising incomes are propelling food and feed demand in the region, boosting corn imports and domestic cultivation.
Europe
Europe presents a mature but stable corn market. Countries such as France, Ukraine, Romania, and Hungary are among the leading corn producers in the region. European nations are increasingly focused on non-GM corn production due to regulatory restrictions and consumer preferences.
The EU’s focus on sustainability and environmental protection is fostering adoption of eco-friendly farming practices in corn cultivation, albeit at a higher cost.
Latin America
Brazil and Argentina are major players in the Latin American corn market, contributing significantly to global exports. Brazil’s second-crop corn (safrinha) has become an essential supply source for Asian markets. The region benefits from abundant arable land, favorable climate, and growing demand for both feed and biofuel applications.
Government support and infrastructure development are helping Latin America expand its corn production footprint.
Middle East and Africa
These regions rely heavily on corn imports due to arid climates and limited arable land. However, increasing investments in irrigation and hybrid seed technologies are improving domestic output in countries like South Africa and Egypt. Corn remains a dietary staple and a strategic commodity for food security in these regions.
Conclusion
The global corn market is poised for sustained growth driven by strong demand for animal feed, renewable energy, and processed food products. Advances in agricultural biotechnology and rising global consumption trends are reinforcing corn’s role as a strategic agricultural commodity.
However, challenges such as price volatility, environmental impact, and competition from alternative crops must be addressed through innovation, sustainable practices, and policy support. With the right balance of technology and regulation, the corn market is expected to remain a cornerstone of global agriculture in the years to come.
𝐌𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐓𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐋𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐬 𝐛𝐲 𝐏𝐨𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐬 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡: